Introduction
In the world of modern medicine, technology has played a remarkable role in revolutionizing the way we diagnose and treat diseases. One such groundbreaking advancement is the Multi-Detector Computed Tomography (CT) Scan, a powerful tool that has transformed medical imaging and greatly improved patient care.
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of Multi-Detector CT scan and understand how this remarkable technology works in simple, easy-to-understand terms.
What is a Multi-Detector CT scan?
A Multi-Detector CT scan, often referred to as MDCT or simply CT scan, is a sophisticated medical imaging technique that utilizes X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the inside of the body. Unlike traditional X-rays, which produce flat, two-dimensional images, MDCT provides highly detailed three-dimensional images, offering a comprehensive view of the body’s internal structures.
How does it work?
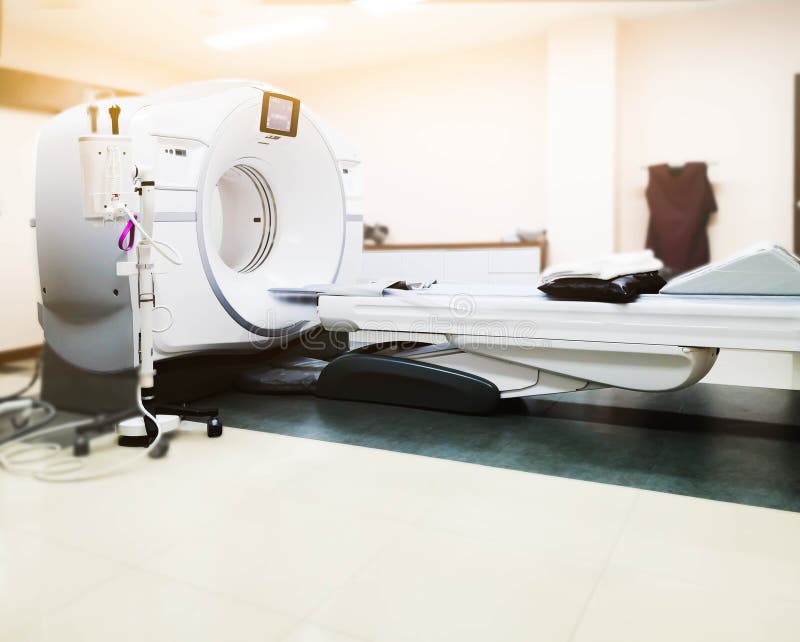
During a CT scan, the patient lies on a special table that moves through a large, doughnut-shaped machine called the CT scanner. The scanner consists of multiple detectors and an X-ray tube that rotates around the patient. As the X-ray tube emits a thin beam of X-rays, the detectors measure how much radiation passes through the body.
The data collected by the detectors is then processed by a powerful computer to reconstruct detailed cross-sectional images or “slices” of the body. These slices are like the pages of a book, allowing doctors to examine different layers of the body with great precision.
Why is it special?
The multi-detector aspect of this technology is what makes it truly remarkable. Traditional CT scanners had only one detector, which limited their ability to capture detailed images quickly. With multiple detectors in a modern MDCT scanner, it can capture numerous slices simultaneously, drastically reducing the time needed for a complete scan.
The speed of MDCT is a game-changer in emergency situations, allowing doctors to rapidly diagnose life-threatening conditions like strokes, internal bleeding, or traumatic injuries. Moreover, the higher resolution and 3D capabilities of MDCT make it invaluable for detecting and diagnosing various medical conditions.
Versatility and Applications
Multi-Detector CT scans find applications in a wide range of medical fields, including:
- Cancer Detection: MDCT can identify tumors and their precise locations, aiding in planning treatment strategies.
- Cardiac Imaging: It helps visualize the heart’s blood vessels and diagnose heart diseases.
- Neurological Conditions: MDCT is used to diagnose brain disorders, such as brain tumors, aneurysms, and stroke.
- Pulmonary Studies: It provides detailed images of the lungs and is essential in diagnosing respiratory issues.
- Orthopedics: MDCT helps evaluate bone fractures, joint problems, and spinal conditions.
Safety Concerns
The radiation exposure from CT scans is a concern, especially for younger patients or those requiring frequent scans. However, modern MDCT machines are equipped with dose-reduction techniques to minimize radiation exposure while maintaining image quality.
It is essential for healthcare providers to weigh the benefits of the scan against the potential risks before performing the procedure.

Conclusion
The advent of Multi-Detector CT scans has revolutionized medical imaging, enabling doctors to diagnose and treat various conditions more effectively. The detailed 3D images obtained through MDCT have become invaluable in clinical practice, providing insights that were once unimaginable.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further refinements in CT imaging, making healthcare more precise, efficient, and patient-friendly. Until then, we can appreciate the wonders of Multi-Detector CT scan, a true marvel of modern medicine.
