Introduction
The heart, often described as the engine of our body, works tirelessly to keep us alive. But have you ever wondered how doctors get a glimpse of its inner workings without opening us up? That’s where Echocardiography comes in – a non-invasive and painless procedure that uses sound waves to create images of the heart. Let’s embark on a journey to explore the wonders of Echocardiography in simple and easy-to-understand language.
What is Echocardiography?
Echocardiography, often called an “echo” for short, is a specialized imaging technique used to visualize the heart’s structure and function. It employs sound waves, similar to those used in ultrasound, to create detailed pictures of the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow.
How does it work?
During an Echocardiogram, a small device called a transducer is placed on the chest. The transducer emits harmless sound waves that bounce off the heart’s structures and return as echoes. These echoes are picked up by the transducer and converted into real-time images displayed on a monitor.
By moving the transducer to different positions on the chest, the doctor can obtain various views of the heart, providing a comprehensive assessment of its health and function.
Advantages of Echocardiography
Echocardiography offers several key benefits:
- Non-Invasive: Echocardiography does not require any incisions or needles, making it a safe and painless procedure for patients.
- Real-Time Imaging: The images are produced in real-time, allowing doctors to see the heart in motion and assess its pumping action and blood flow.
- Detailed Assessment: Echocardiography provides detailed information about the heart’s structure, function, and any abnormalities that may be present.
- Safe and Radiation-Free: Echocardiography does not involve the use of radiation, making it safe for people of all ages, including pregnant women.
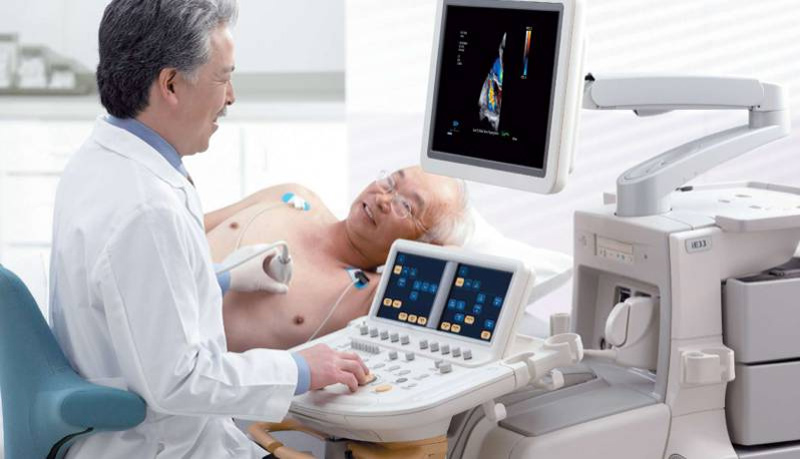
Types of Echocardiography
There are different types of Echocardiography, each serving a specific purpose:
- Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE): This is the most common type, where the transducer is placed on the chest’s surface to obtain images of the heart’s structures.
- Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE): In TEE, a specialized transducer is passed down the throat into the esophagus to get closer and clearer images of the heart.
- Stress Echocardiography: This test involves performing an echocardiogram before and after exercise or medication that stresses the heart. It helps evaluate the heart’s response to stress and detect any underlying coronary artery disease.
Applications of Echocardiography
Echocardiography is used to diagnose and monitor various heart conditions, including:
- Heart Valve Abnormalities: Echocardiography assesses the function and structure of heart valves, helping detect conditions like valve stenosis or regurgitation.
- Congenital Heart Defects: It aids in identifying and evaluating heart defects present at birth.
- Cardiomyopathy: Echocardiography helps diagnose and monitor diseases that affect the heart muscle’s function.
Pericardial Disease: It is used to assess the pericardium, the protective sac around the heart, for conditions like pericarditis or effusion.
Conclusion
Echocardiography is a remarkable tool that allows doctors to see the heart’s secrets without any invasion or radiation. This non-invasive and painless procedure has become an indispensable part of diagnosing and managing various heart conditions.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect further refinements in Echocardiography, making it even more effective in safeguarding our most vital organ – the heart. Until then, we can marvel at the wonders of Echocardiography, a window into the beating core of our existence.
