Introduction
In the world of medical diagnostics, there are specialized tests that help doctors understand how our bodies function. These tests provide valuable insights into our neurological health and respiratory function. Let’s explore the mysteries of EEG, EMG & NCV, and Spirometry and understand how they contribute to better healthcare, using simple and easy-to-understand language.
EEG (Electroencephalogram)
The brain, as the control center of our body, holds many secrets that can be unveiled through an EEG, or Electroencephalogram. This painless and non-invasive test records the electrical activity of the brain.
How does it work?
During an EEG, small metal discs, called electrodes, are placed on the scalp. These electrodes detect and measure the electrical signals generated by the brain’s nerve cells. The signals are then amplified and displayed as waves on a computer screen.
Why is it special?
EEG is special because it helps doctors diagnose and manage various neurological conditions, including epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain injuries. By analyzing the patterns of brain activity, doctors can gain insights into brain function and identify any abnormalities.
EMG & NCV (Electromyography and Nerve Conduction Velocity)
Our muscles and nerves play a crucial role in how our body moves and feels. EMG & NCV are tests used to study the electrical activity of muscles and nerves, helping in the diagnosis of various neuromuscular conditions.
How does it work?
EMG involves inserting tiny needles into specific muscles to record their electrical activity. This provides information about muscle function and detects any nerve-related problems.
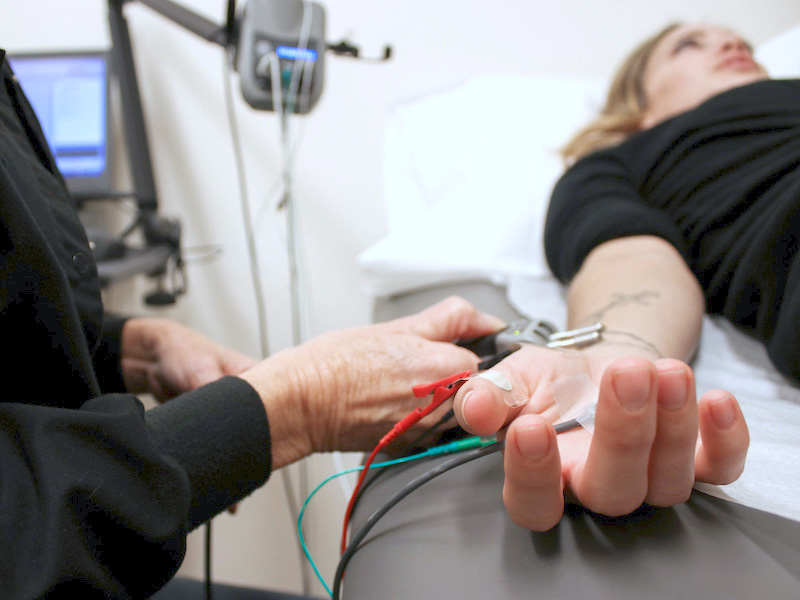
NCV, on the other hand, measures how quickly electrical signals travel through nerves. During the test, small electrical pulses are applied to the skin, and the responses from the nerves are recorded.
Why is it special?
EMG & NCV are special because they help diagnose conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, pinched nerves, and muscle disorders. By understanding the electrical signals in muscles and nerves, doctors can determine the cause of muscle weakness, numbness, or tingling sensations.
Spirometry
Breathing is an essential function of our bodies, and Spirometry is a test that evaluates our respiratory health. This simple and painless test measures how much air we can inhale and exhale and how quickly we can do it.
How does it work?
During Spirometry, you take a deep breath and then blow into a device called a spirometer. The spirometer records the volume of air you exhale and how fast you breathe out.

Why is it special?
Spirometry is special because it helps diagnose and monitor conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other respiratory disorders. By assessing lung function, doctors can recommend appropriate treatments and interventions to improve breathing and overall respiratory health.
Conclusion
EEG, EMG & NCV, and Spirometry are valuable tests that provide valuable insights into our neurological and respiratory health. By understanding the electrical activity of the brain, muscles, and nerves, as well as assessing lung function, doctors can diagnose conditions accurately and tailor treatments to improve our overall well-being.
As medical technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated tests and diagnostic tools that will further enhance our understanding of the human body and lead to better healthcare outcomes. Until then, we can appreciate the wonders of EEG, EMG & NCV, and Spirometry – unraveling the mysteries of our body’s intricate functions.
